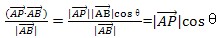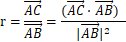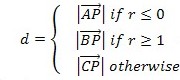计算点到线段最短距离——矢量法
一、思路
矢量算法过程清晰,如果具有一定的空间几何基础,则是解决此类问题时应优先考虑>的方法。当需要计算的数据量很大时,这种方式优势明显。
由于矢量具有方向性,故一些方向的判断直接根据其正负号就可以得知,使得其中的一些问题得以很简单的解决。
根据下图,可以看到,我们只需计算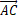 )将其与
)将其与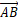 做比较即可分出以下结果。
做比较即可分出以下结果。
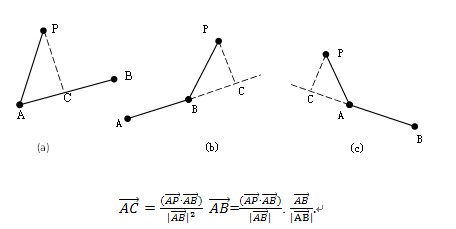
二、步骤
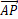 )·
)·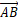 的单位向量,即可得到AC的长度值;
的单位向量,即可得到AC的长度值;
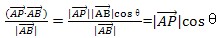
AC的模长与AB的单位向量相乘可以构成AC向量,所以容易得到:
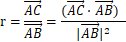
最后,根据其正负以及大小可以判断出三种情况:
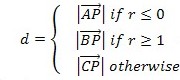
三、代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| class Segment
{
private Point pt1;
private Point pt2;
private double length;
public Segment(Point pt1, Point pt2)
{
this.pt1 = pt1;
this.pt2 = pt2;
double dx = Math.Abs(pt1.X - pt2.X);
double dy = Math.Abs(pt1.Y - pt2.Y);
this.length = Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(dx, 2) + Math.Pow(dy, 2));
}
/// <summary>
/// Finding the shortest distance from a point to the line segment by vector method(矢量法)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="p"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public double Dis2Pt(Point p)
{
//两向量点乘 P:p A:pt1 B:pt2 C:垂足
//矢量法
//不存在垂足C,求与A点距离
double APAB = (pt2.X - pt1.X) * (p.X - pt1.X) + (pt2.Y - pt1.Y) * (p.Y - pt1.Y);
if (APAB <= 0) { return Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow((p.X - pt1.X), 2) + Math.Pow((p.Y - pt1.Y), 2)); }
//不存在垂足C,求与B点距离
double AB2 = Math.Pow(length, 2);
if (APAB >= AB2) { return Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow((p.X - pt2.X), 2) + Math.Pow((p.Y - pt2.Y), 2)); }
//存在垂足C
double r = APAB / AB2;
double Cx = pt1.X + (pt2.X - pt1.X) * r;
double Cy = pt1.Y + (pt2.Y - pt1.Y) * r;
return Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow((p.X - Cx), 2) + Math.Pow((p.Y - Cy), 2));
}
}
|
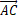 )将其与
)将其与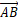 做比较即可分出以下结果。
做比较即可分出以下结果。
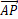 )·
)·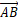 的单位向量,即可得到AC的长度值;
的单位向量,即可得到AC的长度值;